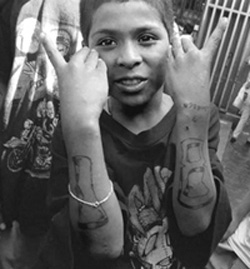
Southwest Tribune Newspaper
Rochester, NY- The issue of impoverished inner city youths joining gangs is a complex social problem that has been present in many societies around the world for a long time. While I can provide some general insights, it's important to note that specific factors and circumstances can vary from one community to another.
Several factors contribute to the phenomenon of impoverished inner city youths joining gangs:
1. Socioeconomic conditions: Poverty, lack of educational opportunities, limited access to healthcare, and high unemployment rates are often prevalent in inner city areas. These conditions can create a sense of hopelessness and desperation among young people, leading them to seek alternatives for survival and a sense of belonging.
2. Lack of positive role models: In some cases, there may be a lack of positive role models in these communities, making it difficult for young individuals to find guidance and inspiration. Without positive influences, they may turn to gangs for a sense of community, protection, and mentorship.
3. Peer pressure: The desire to fit in and gain acceptance among peers can lead vulnerable individuals to join gangs. Gangs often offer a sense of identity, camaraderie, and protection, making them an attractive option for young people seeking validation and support.
4. Exposure to violence: Growing up in environments where violence is prevalent can desensitize young individuals to its consequences and make them more likely to resort to violence as a means of problem-solving or self-protection.
Addressing the issue of impoverished inner city youths joining gangs requires a multifaceted approach involving various stakeholders, including community organizations, law enforcement, educational institutions, and government agencies. Some potential strategies include:
1. Education and job opportunities: Providing quality education and vocational training programs can equip young people with the necessary skills to find stable employment and break the cycle of poverty.
2. Mentoring and positive role models: Establishing mentoring programs and initiatives that connect young people with positive role models from their communities can offer guidance, support, and positive examples for them to emulate.
3. Community outreach and engagement: Strengthening community organizations, creating safe spaces, and organizing recreational and educational activities can help foster a sense of belonging and provide alternatives to gang involvement.
4. Violence prevention and intervention: Implementing violence prevention programs that address the root causes of violence and provide conflict resolution skills can help break the cycle of violence and reduce the appeal of gangs.
5. Collaboration between stakeholders: Collaboration between community leaders, law enforcement agencies, schools, and social services is crucial to effectively address the issue. By working together, these stakeholders can share resources, coordinate efforts, and implement comprehensive strategies.
It's important to recognize that every community is unique, and tailored approaches are necessary to address the specific challenges faced by impoverished inner city youths. Long-term commitment, investment, and a holistic approach are necessary to create lasting change and provide viable alternatives for young people at risk of joining gangs.





